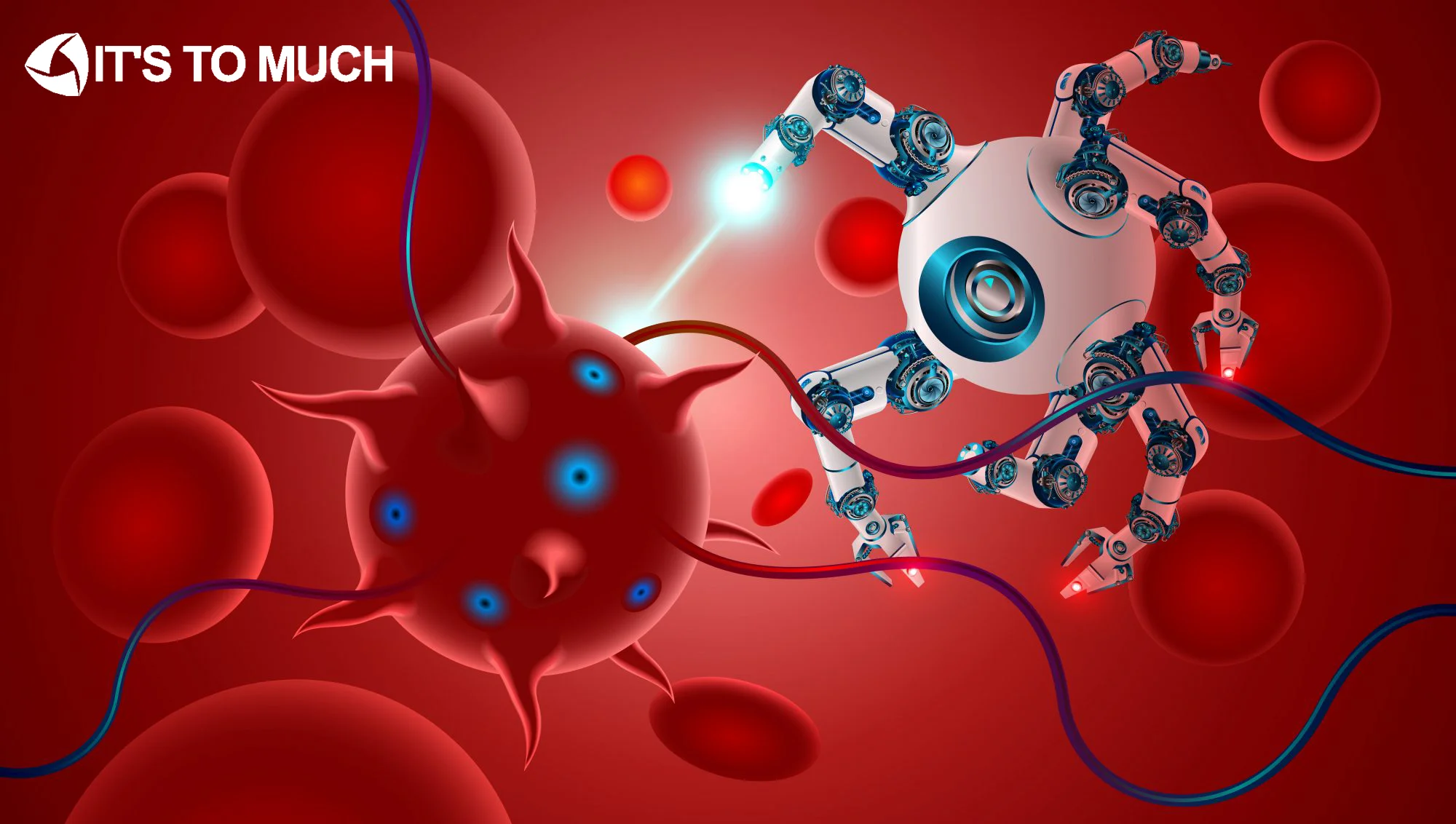
Tiny robots navigating blood vessels
One of the most catastrophic medical emergencies in the world is still stroke. Due to inefficient or delayed therapies, patients frequently experience permanent disability. New developments of tiny robots navigating blood vessels in medical robotics provide creative answers to this problem. With their ability to maneuver through complex blood veins, tiny robots offer precise medical care. Researchers are working on creating micro-robots that can navigate veins and arteries with ease. These gadgets have the ability to directly administer tailored treatments to damaged brain regions. Recovery prospects increase when the interval between diagnosis and intervention is shortened. Conventional therapies frequently depend on invasive surgery or widespread drug delivery.
Tiny robots navigating blood vessels promises less invasiveness and quicker stroke recovery. By precisely focusing on clogged arteries, tiny robots reduce collateral damage. Scientists hope that these robots will remove blood clots with the least amount of harm to the patient. Robotic systems can also transport medications that more efficiently break up clots. Robot size, movement, and reactivity are being optimized for human anatomy by engineers. These advancements represent a change in stroke therapy from reactive to extremely proactive. Robotic navigation systems have the potential to significantly increase patient survival rates in hospitals.
How Tiny Robots Work Inside Blood Vessels
Advanced materials are essential for blood vessel navigation micro-robots. They move accurately inside arteries thanks to magnetic fields and biocompatible coatings. Because of their modest size, the robots do not impede blood flow while traveling. Real-time monitoring of blood pressure and vascular health is made possible by embedded sensors. Some designs use tiny cameras that give surgeons real-time visual feedback. Robots use AI algorithms to dynamically modify their mobility in order to negotiate intricate courses. In order to efficiently combat blood flow resistance, researchers optimize propulsion systems. The robots can transport therapeutic payloads, like as stents or drugs that dissolve clots. Before human clinical trials start, engineers evaluate them in virtual vasculature.
After use, safety features guarantee that robots return safely or deteriorate harmlessly. The precision of treatment is significantly increased when robots and imaging approaches are combined. Micro-robots revolutionize medical intervention by fusing AI, sensors, and intelligent materials. These developments represent a major breakthrough in minimally invasive medical technology. These small robots may eventually be able to effectively manage several stroke therapies at once.
Potential Impact on Stroke Recovery
Early intervention and targeted treatment delivery are essential for stroke recovery. Compared to existing techniques, tiny robots may be able to treat strokes more quickly. They lower the chance of secondary brain injury by actively attacking clots. Patients might return to their regular lives more quickly and have shorter hospital stays. Compared to systemic medications, the accuracy of robotic intervention reduces side effects. Medication can be administered by robots at precise problem sites in regulated dosages. After treatment, researchers anticipate notable gains in motor and cognitive performance. Reducing invasiveness improves patient comfort during recuperation and reduces the danger of infection. Reduced demand for rehabilitative therapy may result in lower long-term healthcare expenses.
Patients who arrive late to hospitals may get longer treatment windows thanks to micro-robots. Additionally, they could support high-risk patients’ preventive measures. Hospitals may start using these robots as standard care when recovery rates rise. Combining robotic intervention with conventional therapy may be beneficial for patients. Tiny robots have the potential to improve the prognosis of stroke for millions of people globally.
Challenges in Implementing Tiny Robot Treatments
Micro-robot treatments still confront a number of technological obstacles despite their considerable potential. It is difficult to design robots that are safe and useful inside blood arteries. Precise navigation and propulsion against blood flow call for sophisticated engineering solutions. It’s still difficult to guarantee long-term biocompatibility without triggering immunological responses. It is challenging to produce these devices at scale while preserving dependability. It may take several years for new medical robotics to receive regulatory approval. To properly handle and oversee robotic therapies, hospitals require qualified staff. Patients in areas with minimal resources may first find it difficult to receive care due to high prices. Remote-controlled interventions within human bodies raise ethical questions.
Researchers keep improving the robustness of robots while making sure they don’t harm vessels. Integration with AI and imaging systems necessitates significant infrastructure and computational support. Clinical trials must demonstrate both improved patient outcomes and safety. Adoption rates may be impacted by public opinion and acceptance of internal robots. Before extensive deployment is possible, it is imperative to address these issues.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Tiny robotic stroke treatments appear to have a very bright and revolutionary future. To treat several locations at once, researchers are investigating swarms of micro-robots. These gadgets could be further reduced in size for even less intrusive operations thanks to nanotechnology. AI integration will enable independent decision-making in challenging medical situations. Robots could deliver a variety of treatments, such as neuroprotective medications and clot clearance. Smart sensors have the ability to identify stroke symptoms early and take prompt action. Telemedicine and robotics could provide stroke therapy in far-off places. Robots that are biodegradable might completely do away with the necessity for retrieval processes. Innovation will advance more quickly when engineers, neurologists, and AI specialists work together.
Robots that monitor patients over an extended period of time could track their progress and make dynamic therapeutic adjustments. Insurance companies might encourage hospitals to use robotic stroke treatments. Adoption on a global scale could greatly lower stroke-related fatalities and disabilities. Additionally, scientists are investigating the integration of these robots with genetic and regenerative treatments. All things considered, the field is moving toward more accurate, proactive, and successful stroke care.
Conclusion
Medical technology has advanced significantly with tiny robots exploring blood arteries. They redefine stroke therapy approaches by offering focused, minimally invasive therapies. Preliminary research indicates the possibility of improved results, a quicker recovery, and fewer adverse effects. Before broad use, there are still issues with design, pricing, and regulatory approval. Ongoing research promises creative ways to effectively get over these obstacles. Future advancements could smoothly combine improved medicines, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Technology and medicine together open up previously unthinkable possibilities. By using these technologies, hospitals may raise the bar for stroke care worldwide. These developments will help patients, physicians, and healthcare systems.
Small robotic treatments have the potential to completely transform the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of strokes. The goal of completely automated stroke treatment is getting closer as research advances. This technology is a symbol of precision, hope, and a revolutionary medical future. In the end, tiny robots have the potential to improve global health outcomes and save countless lives. The time of sophisticated, minimally invasive stroke therapy is drawing near. In order to administer tailored medicines, researchers use Tiny robots navigating blood vessels.

I’m a passionate blogger and senior website developer with an MPhil in Computer Science, blending technical expertise with a deep appreciation for the art of storytelling. With advanced knowledge of English literature, I craft content that bridges creativity and technology, offering readers valuable insights and engaging narratives. Whether building dynamic websites or exploring thought-provoking ideas through my blog, I’m driven by a commitment to innovation, clarity, and impactful communication.