Space Exploration
Introduction: Space Exploration Becomes Global Power Stage
These days, space exploration clearly influences the competition for global supremacy. To achieve technical leadership, nations make significant investments. Governments consider space to be strategically important. Space missions are an indication of both scientific and economic power. Launches are a way for nations to show their ability for innovation. Additionally, space initiatives foster togetherness and pride in the country. Orbital accomplishments are becoming more and more important in contemporary geopolitics. These days, satellites help with intelligence, communication, and defense objectives. Countries want to have their own launch capability. They lessen the need for foreign space services. Success in space enhances global diplomatic prestige. Traditional space leaders are now under threat from emerging nations. Private businesses have an impact on international competition.
Their collaborations alter national strategies. To demonstrate their importance, governments finance ambitious projects. Space has evolved into a testing ground for cooperation and competition. Competition spurs more ambitious objectives and quicker invention. During speeches, political leaders make reference to space progress. People see success in space as a national accomplishment. Media attention magnifies narratives of competition. There are now economic and security aspects to the space race. To secure long-term benefits, global powers make investments. Space exploration is a reflection of larger power battles. Modern international relations are defined by this changing environment.
Major Powers Compete for Strategic Space Dominance
The United States is still at the forefront of advanced missions. NASA collaborates on innovative projects with private businesses. China’s aspirations for Mars and the moon are growing quickly. Its space stations exhibit increasing technological assurance. Despite financial difficulties, Russia retains its historical competence. Through the European Space Agency, Europe enhances collaboration. India expands its missions using economical tactics. Every country aspires to have its own launch capability. Satellite control guarantees the security of communications. Space is important to military planners because it provides advantages for observation. Countries thoroughly test anti-satellite technologies. Orbital conflict is a concern in light of these measures. Dominance in space now facilitates military planning on land. To ensure technological dominance, governments finance research.
Spending on space has become a higher priority in national budgets. Political leaders associate national status with space achievement. Shared missions increase diplomatic impact. Space exploration initiatives give rise to alliances. Competition drives quicker cycles of innovation. Domestic industries benefit from technology transfers. International tensions also rise as a result of strategic rivalry. There are still few guidelines for behavior in space. To obtain an advantage, nations push boundaries. Geopolitical rivalry extends into space. Future global power balances are shaped by this competition.
Commercial Space Firms Reshape Global Competition
Significant breakthroughs in space are currently driven by private companies. Businesses deploy satellites for less money. Reusable rockets alter the viability of a business. Private launch companies are essential to governments. Commercial rivalry quickens cycles of innovation. Businesses actively seek for satellite internet networks. These networks offer digital connectivity on a worldwide scale. They are considered strategic infrastructure by governments. Defense contracts are also supported by private companies. Space tourism increases visibility and financial worth. The aircraft industry is seeing an upsurge in investment flows. Startups are able to secure finance for technological exploration. Competition improves access and reduces expenses. Through policy incentives, nations encourage domestic businesses. Public-private collaborations increase the scope of missions.
Success in business increases a country’s influence outside. Due to demand, space markets are expanding quickly. Orbit-based data services generate new enterprises. Governments are under pressure to change due to private innovation. In order to control growth, regulatory frameworks change. Space capabilities and economic power are now closely related. Corporate success affects a country’s geopolitical position. Commercial space turns into a soft power tool.
Space Technology Shapes Security and Surveillance Strategies
Real-time intelligence gathering is now possible thanks to satellites. Orbital assets are essential to military operations. These days, navigation technologies provide precise guidance for weapons. Satellites for communication provide worldwide command networks. Early warning systems identify possible dangers. In times of conflict, space assets offer strategic advantages. Governments use defensive measures to safeguard satellites. For space systems, cybersecurity becomes crucial. To prevent interruptions, nations create redundancies. Congestion raises the chance of space debris. Countries keep a close eye on orbital activity. The ability to monitor has an impact on diplomatic discussions. Planning for national defense benefits from space awareness. Intelligence organizations heavily incorporate satellite data. Having control over space assets makes deterrence stronger.
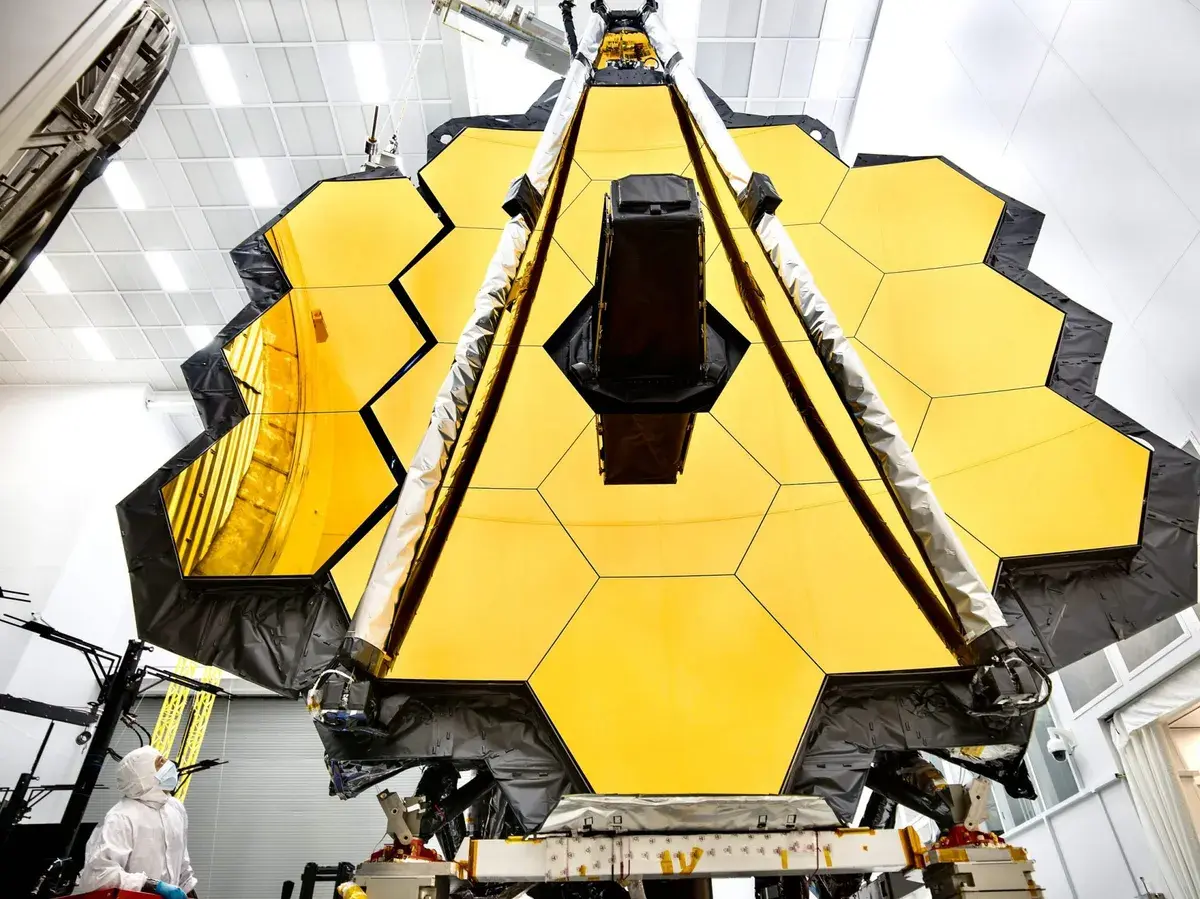

Countries make investments in robust satellite systems. Space operations are increasingly part of military concepts. Stable orbital settings are essential for global security. Space-related concerns are becoming more prevalent in discussions about arms control. In this area, international trust is still brittle. Competition in security accelerates technical advancement. Strategic leverage is now equivalent to space power.
Future Outlook: Cooperation Versus Competition in Space
Shared governance is essential to space’s future. Debris management is one of the major problems that nations face. Cooperation can lower expenses and dangers. Collaborative missions foster confidence between adversaries. International accords have the power to encourage ethical conduct. Nonetheless, competition keeps pushing the pace of discovery. Success in space is a way for emerging nations to gain prominence. Shared satellite data is necessary for climate monitoring. Space exploration helps achieve global sustainability objectives. International research initiatives are beneficial to education. Space law needs to change as technology does. Concerns about militarization are becoming more ethical. Stability still depends on diplomatic communication. Projects that include collaboration can reduce political tensions. Shared knowledge is beneficial to scientific advancement.
Decisions about policy will be influenced by commercial interests. Cooperation that is balanced helps stop conflicts from getting worse. Peaceful exploration initiatives benefit humanity. The space arena is a reflection of global dynamics. Vision and accountability are necessary for leadership. Future generations will inherit the choices made today. Global power dynamics will be defined by space exploration.