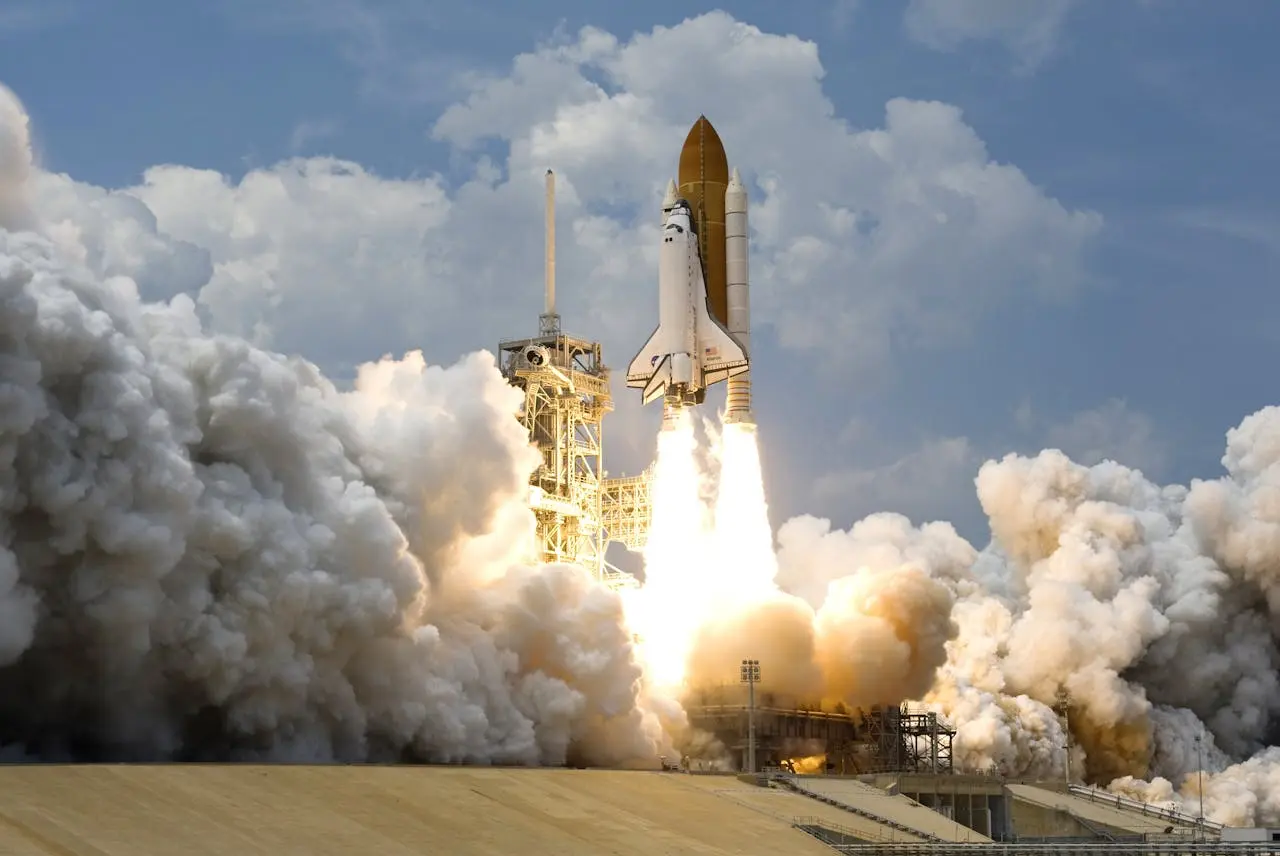
Advancements in technology and ambitious exploration goals are necessary to future of space travel at a rapid pace. A new era of human space exploration is on the horizon. Emerging technology is changing how humans get to, explore, and inhabit distant worlds. Private businesses and governments are blazing the trail, with their sights set on the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
Revolutionizing Spacecraft: Faster, Smarter, and More Efficient Technologies

Modern spacecraft, now all very fast, intelligent, and fuel-efficient, are completely transforming the latter. Conventional chemical rockets are being replaced with innovative propulsion methods. With ion propulsion, nuclear thermal propulsion, and antimatter propulsion longer travel times and more efficiency is possible. Ion propulsion engines use electric fields to accelerate charged particles for thrust. They are more effective than chemical propulsion. NASA’s Deep Space 1 and Dawn probes have successfully proved this technology. Future of space travel that venture out to deep space will use similar engines.
Hydrogen fuel is heated in nuclear reactors to produce thrust in nuclear thermal propulsion systems. This technology could massively decrease travel time to Mars. Further down the line, NASA is collaborating with DARPA on nuclear propulsion systems for upcoming missions. They are exposed to less radiation when they move faster. While it’s yet theoretical, antimatter propulsion could make interplanetary travel possible at unprecedented speeds. Because they release huge amounts of energy, antimatter processes are ideal for long-distance space travel. Researchers are studying effective ways to harness this power.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reducing the requirement for human interaction by enhancing spacecraft autonomy AI-powered navigation systems are improving the efficiency, safety, and decision-making of the environments they guide. NASA’s Perseverance rover explores Martian tracks using artificial intelligence with minimal human support. Future missions are aided by using AI to improve efficiency. 3D printing is revolutionizing spaceship production, cutting costs, and expanding design freedom. Space agencies are testing the 3D-printed generation of rocket parts and components. In the future, tools, homes, and even food could be 3D printed in space for humans.
Colonizing Other Planets: The Next Step for Humanity
Colonization of distant planets (which was previously a thing of sci-fi fantasy) is becoming a possibility! For scenarios in other worlds, scientists and engineers are developing sustainable living systems. Mars and the Moon are the prime destinations for human colonization. Lunar colonization will serve as a springboard for Mars missions. NASA’s Artemis program aims to establish a permanent base on the moon. The Moon, in its proximity, is ideal for testing long-term living in space.
Lunar ice deposits and other resources can meet oxygen and water needs. Some of the biggest barriers to colonizing Mars are its thin atmosphere, radiation, and boiling temperatures. SpaceX is shooting for a mission to put people on Mars in a few decades. The man who tweets solutions to global warming Lotus still Tesla wants colonies on Mars that are powered by natural resources and solar energy.
Terraforming Mars: The idea behind terraforming Mars in the long run is to change the atmosphere of Mars so that it becomes habitable. Say scientists: To release greenhouse gases to trap heat and thicken the atmosphere. Terraforming remains a daunting, distant goal, however. Self-sustaining habitats are key for long-term survival in other worlds. Researchers are working on closed-loop life support systems to recycle food, water, and air. Hydroponic and aeroponic farming could potentially provide fresh produce for astronauts.
In the future of space travel, colonies can only thrive with the balancing act of resource consumption. Robotic infrastructure to build habitats and stock supplies ahead of human settlers. Self-sufficient robots will supply power, bore ice for water, and build shelters. AI will also be vital to off-world colonization in robotic helpers.
Commercial Space Travel: Making Space Accessible to Everyone

Commercial space travel, which opens space to private companies and citizens, is changing the sector. Private space missions, orbiting hotels, and space tourism are not just pie-in-the-sky dreams anymore. Companies like Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin, and SpaceX are leading this movement. Commercial space travel starts with suborbital tourism. Both Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo and Blue Origin’s New Shepard offer short trips to space. Such flights offer passengers weightlessness and breathtaking views of Earth. While still pricey, ticket prices should eventually decrease. Orbital space hotels will redefine luxury travel.
Companies such as Orbital Assembly and Axiom Space are designing space habitats for tourists. Space hotels of the future will offer Earth observation lounges, private cabins, and artificial gravity. Space travel may become an actual thing in a few decades. The purpose of SpaceX’s Starship is to shuttle people and spacecraft between worlds. Future of space travel science suggests ordinary folks will travel between planets. Advanced life support systems will allow safe long-duration spaceflights. The study of microgravity on commercial spaceflights is opening up new frontiers in scientific research. Pharmaceutical companies conduct space trials to develop pioneering drugs.
In medicine, it may lead to radical breakthroughs. Commercial space stations will undergo development, creating new industrial and research opportunities for private-sector enterprises. Such microgravity environments will benefit industries ranging from materials research to electronics to biotechnology. Commercial partnerships will accelerate developments in space technology
AI and Robotics: Transforming Space Exploration and Colonization
Robots and artificial intelligence are taken for granted in modern space exploration. A systems approach is also essential to managing deep space missions and, in order to improve operational capability and safety, systems and subsystems will need to rely on autonomy in terms of their operations to enhance overall mission efficiency. Nobody can live in the inhospitable environments these robots and AI-infused spacecraft are exploring.
PERSEVERANCE: AI helps NASA’s rovers navigate Martian terrain autonomously. AI decision-making enables the inline (real-time) changes without human intervention. Those new rovers will have advanced AI that will allow them to perform complex scientific investigations autonomously.
Device-fueled explorers — the Rosalind Franklin rover of the European Space Agency, for example — are designed to hunt for signs of life on Mars. Devices powered by artificial intelligence inspect air conditions and soil samples. These discoveries will shape future space missions. So humanoid robots, like NASA’s Valkyrie, are being constructed to assist humans in space. They can operate machinery, perform maintenance, and respond to emergencies. Robotic helpers will accompany human explorers on trips in the future.
AI-powered spacecraft will make interstellar travel possible without human crews. The systems will be self-optimizing based on mission success, energy use, and navigation. But there may be a high-tech solution: Artificial intelligence-powered spacecraft could scour exoplanets, search for alien life, and even reach other galaxies.
Swarm robotics will enhance planetary exploration through the deployment of many small robots that act in concert. Capable of constructing infrastructure, collecting data, and surveying terrains, these robotic swarms can cover vast distances. Swarm intelligence will revolutionize space missions.
Interstellar Travel: Reaching Beyond Our Solar System

Interstellar travel is still one of the greatest challenges to humanity. The distances between stars are so great that new propulsion systems will be required. Ideas being explored include solar sails, warp drives, and fusion propulsion. Warp-drive technology inspired by Einstein’s theories might make faster-than-light travel possible. Alcubierre drive There are many different types of space drives, but the idea behind the Alcubierre drive is that in order to make future of space travel more effective, we need to manipulate space-time. While theoretical, it holds promise for interplanetary missions.
Solar sails employ the momentum of photons to propel spacecraft. LightSail 2 successfully tested this technique in Earth orbit. Future solar sail missions could potentially allow travel over vast distances, without reliance on conventional fuel. Fusion propulsion has the promise of providing immense thrust for interplanetary missions, leveraging nuclear fusion reactions. Interstellar spacecraft might run on deuterium and helium-3 fuels. The workability of the approach is still being explored. So-called suspended animation or cryogenic sleep could enable explorers to survive long intergalactic journeys.
Scientists are exploring safe metabolism-slowing approaches. This could revolutionize deep-space missions. Breakthrough Starshot and similar interstellar missions dream of sending miniature spacecraft to Alpha Centauri. Laser-driven light sails could propel the probes at a significant fraction of the speed of light. These trips could shake up views of exoplanets up close for the first time.
The Search for Extraterrestrial Life: Expanding Humanity’s Understanding of the Universe
The search for aliens is the main driver of outer space investigation. Scientists are studying extremophiles on Earth, deep-space signals, and exoplanets. The discovery of extraterrestrial life, if that ever occurs, would be a definitive turning point. Exoplanet research has discovered thousands of planets that lie in the habitable zones of distant stars. The James Webb Space Telescope is studying their atmospheres for biosignatures. Signs of life may be detected in the coming decades.
SETI (Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence) programs are searching for signals from extraterrestrial life. Radio telescopes pick up unusual broadcasts that might be a sign of intelligent civilizations. Breakthrough Listen, is a major project searching for communications from extraterrestrials. Astrobiology studies the viability of life on that one in a billion chance that it survives in hostile ecosystems. What Scientists Say When They Find Creatures That Live in Antarctic Ice and Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents Such findings help understand where life might exist outside Earth. We search for microbiological life on cold worlds like Europa, and Enceladus.
NASA’s Europa Clipper will pore over its subterranean ocean for signs of biological activity. Liquid water is a good indication that life exists in it and is more common in our solar system. Mars sample return missions will bring Martian dirt back to Earth to study. These samples may show past or present microbial life. If we find life on Mars, our understanding of biology might shift.
Conclusion: A Bold Future Awaits Humanity in Space
The future of space travel is full of wonderful possibilities. Advances in technology are accelerating, making space travel safer and more effective. Interstellar travel, colonizing planets, and searching for extraterrestrial life become achievable goals. As technology evolves, humanity’s reach into the cosmos will continue to expand. Natural Discoveries in the Space Exploration Per Episode Will Lead Over Groundbreaking Century The dream of becoming an interplanetary species is closer than ever.

I’m a passionate blogger and senior website developer with an MPhil in Computer Science, blending technical expertise with a deep appreciation for the art of storytelling. With advanced knowledge of English literature, I craft content that bridges creativity and technology, offering readers valuable insights and engaging narratives. Whether building dynamic websites or exploring thought-provoking ideas through my blog, I’m driven by a commitment to innovation, clarity, and impactful communication.