Green Data Centers
Green Data Centers Transform Global Cloud Infrastructure Sustainability
Through more intelligent energy use and design, green data centers are currently driving sustainable cloud infrastructure innovation globally. Businesses want effective computing that decreases operating costs and emissions. These days, data centers use enormous amounts of electricity worldwide every year. In response, operators implement efficient cooling systems and cleaner power. They put sustainability first without compromising dependability or performance. Governments encourage this change by enacting environmental laws and providing incentives. In order to fulfill their corporate responsibility objectives, businesses often look for greener hosting. In order to compete, cloud providers highlight their reduced carbon footprints. They make significant global investments in the procurement of renewable energy. These days, a lot of establishments use hydro, wind, and solar energy.
These decisions greatly lessen reliance on fossil fuels. In order to maximize airflow and lower cooling demand, operators alter layouts. Additionally, they use sophisticated monitoring technologies to track efficiency in real time. These developments reduce their negative effects on the environment while increasing uptime. These days, new digital infrastructure initiatives are defined by sustainable data centers. They promote the expansion of digital technology worldwide without wasting a lot of energy. This change influences how businesses handle cloud expansion in an ethical manner.
Energy Efficient Architecture Redefines Modern Data Center Design
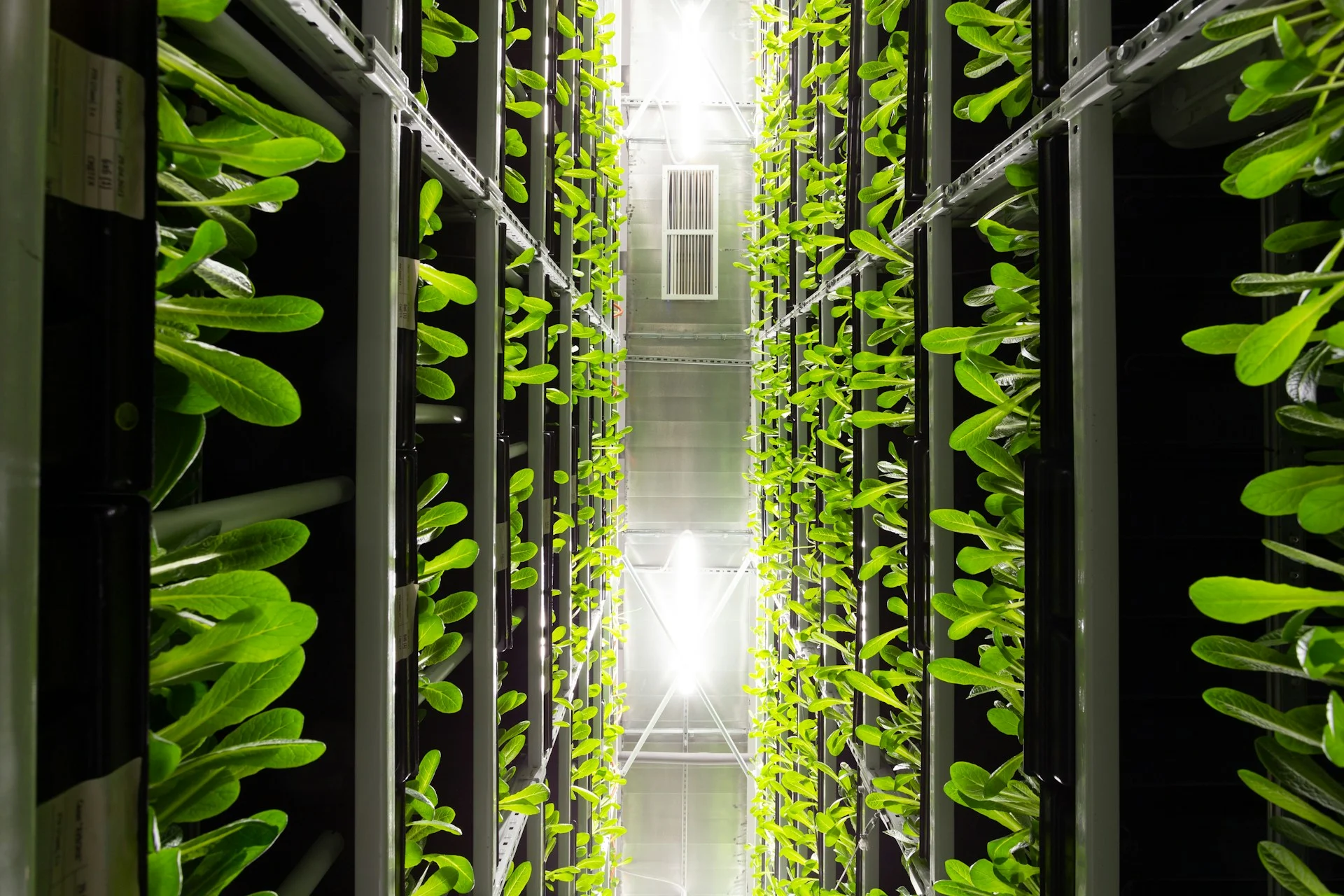
The development of green data centers heavily relies on energy-efficient construction. In order to reduce energy loss and heat generation, engineers design buildings. They employ modular layouts, which enhance scalability and airflow control. Containment of hot and cold aisles significantly increases cooling efficiency. To lower conversion losses, operators install high-efficiency power distribution units. They choose low-power servers that maximize performance per watt. Additionally, building materials help the objectives of thermal stability and insulation. Nowadays, when the weather permits, many centers employ natural cooling techniques. Free air cooling greatly lessens the need for mechanical chillers. In dense situations, liquid cooling technologies improve thermal efficiency even more. To reduce transmission losses, designers locate facilities close to renewable energy sources. Automation systems dynamically modify cooling and electricity loads on a continuous basis.
During times of high demand, these systems guarantee peak performance. Smart sensors instantly identify inefficiencies and take necessary action. Without compromising dependability, this architectural evolution allows for sustainable growth. Globally, competitive cloud infrastructure is now defined by energy-efficient design.

Renewable Energy Integration Accelerates Sustainable Cloud Operations
The inclusion of renewable energy powers contemporary data centers’ sustainability objectives. Operators and sustainable energy suppliers enter into long-term power purchase agreements. These agreements lower carbon exposure and stabilize energy prices. Worldwide, hyperscale buildings are being powered by solar farms and wind parks. Some businesses make direct investments in assets used for renewable energy. Others encourage neighborhood energy initiatives to counteract consumption. When supply fluctuates, energy storage technologies improve dependability. Batteries store extra energy for times when demand is at its highest. Tools for grid interaction efficiently distribute loads among regions. Many data centers use renewable sourcing techniques to become carbon neutral.
For potential future applications, operators also investigate hydrogen and biofuel options. These substitutes offer more scalability and less emissions. Corporate sustainability reporting standards are supported by renewable integration. Additionally, it enhances the brand’s reputation among consumers who care about the environment. Visible climate pledges provide cloud providers a competitive edge. Adoption of renewable energy now characterizes responsible leadership in cloud infrastructure.
Advanced Cooling Technologies Reduce Environmental Impact Significantly
Modern cooling solutions are essential to the effectiveness of green data centers. Traditionally, cooling systems use a significant amount of facility energy. The goal of contemporary designs is to significantly lessen this strain. Compared to air systems, liquid cooling transfers heat more effectively. It efficiently supports computing environments with high densities. Hardware is submerged in nonconductive fluids for immersion cooling. Heat is quickly and uniformly removed with this technique. When the weather is favorable, free cooling makes use of outside air. This strategy reduces electricity consumption throughout the year. AI-powered cooling control continuously improves temperature settings. Real-time data from sensors allows for adaptive modifications.
These innovations stop energy waste and overcooling. Systems for recovering waste heat repurpose heat for adjacent facilities. This reuse helps with industrial processes or district heating. Cooling innovation simultaneously lowers carbon emissions and operating expenses. These advancements make it possible for cloud infrastructure to scale sustainably on a global scale.
Digital Monitoring And AI Optimize Sustainable Data Center Performance
AI and digital monitoring improve sustainability in contemporary data centers. Intelligent platforms regularly examine trends in power consumption. They find inefficiencies before they have an effect on operations. AI anticipates spikes in demand and makes proactive resource adjustments. During times of low utilization, this capacity stops energy waste. Machine learning models maximize server-to-server workload distribution. These versions cut down on needless usage and idle capacity. Tools for predictive maintenance help avoid equipment malfunctions and downtime. They also lessen the need for replacements and increase the lifespan of hardware. Environmental performance measures are transparent thanks to real-time dashboards.
Operators are more accurate in tracking the effectiveness of carbon utilization. Power, cooling, and lighting are all quickly adjusted by automated controls. All procedures will be consistently efficient thanks to this automation. Long-term sustainability planning benefits from data-driven decision-making. Integration of AI improves operational excellence and resilience. Sustainable cloud infrastructure solutions are now based on digital intelligence.
Global Policies And Industry Collaboration Drive Green Adoption
Worldwide adoption of green data centers is accelerated by international cooperation and policies. Governments set goals for reducing emissions and establishing energy efficiency standards. Incentives promote funding for environmentally friendly infrastructure initiatives. Industry partnerships freely exchange technological advancements and best practices. Cloud providers work together on procurement strategies for renewable energy. Standards organizations create sustainable performance benchmarks. Across the industry, compliance is the driving force behind ongoing development. Public reporting improves accountability and transparency.
Environmentally conscious cloud services are becoming more and more popular. Providers are under pressure from this requirement to implement more environmentally friendly practices. Utility partnerships enhance the integration of renewable energy sources and system stability. Technological advancements in energy management are a result of research institutions. Collaboration across industries speeds up sustainable change. Together, these initiatives bring environmental responsibility and economic progress into harmony. These days, green data centers stand for a worldwide dedication to sustainability. They influence the development of responsible digital infrastructure in the future.