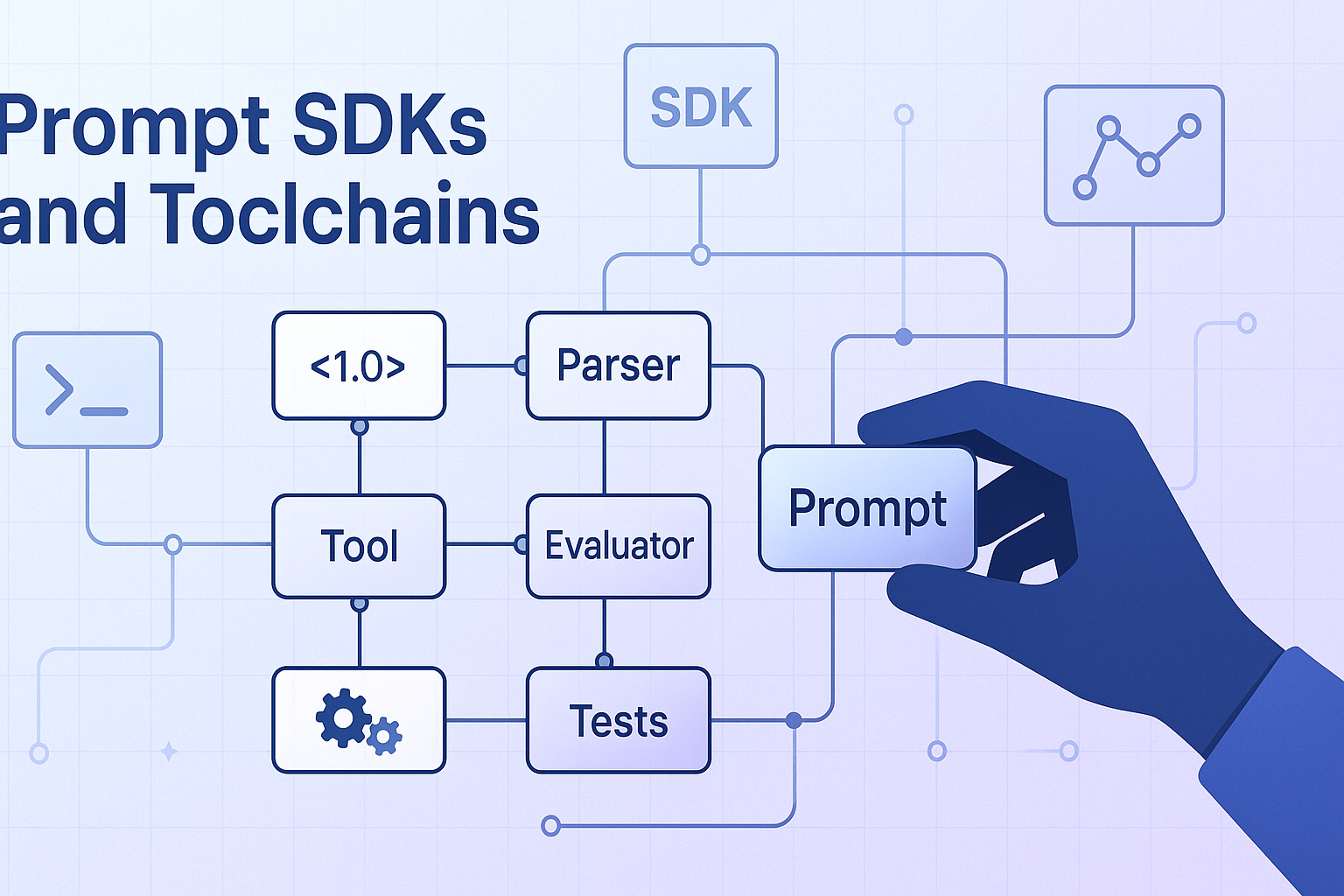
Using Prompts Like Code Modules
Artificial intelligence is getting better at more than just writing text. Prompts are now digital assets that may be used again, are modular, and are organized. This progress changes how developers make and manage AI workflows. SDKs and toolchains that come out on time make it possible to change things quickly and correctly. They don’t see prompts as just text instructions; they see them as programmable units. You can add, test, and version each prompt just like you can with software code. This methodical approach guarantees better cooperation, scalability, and consistency. Developers can easily keep their logic consistent across a wide range of AI applications. Prompt SDKs make creative AI development more structured and easier to repeat. Toolchains make debugging, deployment, and performance optimization much easier. Together, they change the way AI engineering will be done in the future. In 2025, prompts will work like reliable, easy-to-use software parts.
Using Prompts Like Code Modules: The Growth of Prompt Engineering
At first, prompt engineering was a creative and experimental way to do things. Early engineers wrote long, detailed instructions for AI systems. These prompts were meant to get more accurate and context-aware answers. But it rapidly proved hard to keep track of prompts for more than one project. Even small adjustments to the phrases could have a big effect on how well the model works. Teams had a hard time keeping things consistent and controlling changes to the prompt designs. As things got more complicated, it became clear that better structure was needed. Developers found that prompts needed the same level of discipline as conventional software coding.
This understanding led to the idea of “prompt as code.” It put a lot of focus on versioning, testing, and modularity in managing prompts. The change marked a major shift in how AI is developed all across the world. Prompt engineering grew out of improvisation and became a structured sector of technology.
What are SDKs for prompts?
Prompt SDKs give you a structured way to handle AI prompts in a way that works. Like software components, they let developers make, test, and use prompts. Every prompt becomes a piece of logic that may be programmed, broken down into smaller parts, and used again. This approach replaces static text with dynamic, maintainable prompt structures. Developers can quickly get version prompts, change tracking, and consistent performance. Integrated debugging, analytics, and validation tools make workflows more reliable. Prompt SDKs also offer secure version control systems and collaborative editing. They make it easier to manage intricate prompts across teams and contexts. SDKs reduce confusion and duplicate work by using software-like discipline. Businesses benefit from prompt lifecycles that can be scaled, tracked, and audited. In short, prompt SDKs give AI prompting structure and make sure it works correctly. They turn creative instructions into dependable, code-based tools.
Code Modules for Prompts
When prompts act as code modules, they are like structured program components. Every question clearly states what inputs are needed, what the logical steps are, and what the anticipated outcomes are. With this structure, prompting becomes a methodical and repeatable field of engineering. For instance, a prompt for sentiment analysis becomes a standard function that may be used again and again. Teams may use it with other AI apps, change its settings, and bring it in. In large systems, these kinds of modular prompts cut down on duplication and make maintenance easier. They make it easier to develop things that can be utilized in many different situations with only one prompt. Developers may easily test, improve, or replace modules without stopping workflows.
This organized method makes sure that all of the machine learning pipelines are the same. Modular prompts also make it easier to work together on iterative cycles, keep things clear, and keep track of different versions. By thinking about prompts as code, teams may combine technical correctness and creativity in a useful way.
Why You Should Treat Prompts Like Code
When you treat prompts like code, you start to use a logical, modular approach to development. This framework makes projects more reusable, easier to manage, and more consistent with each other. Teams may share, change, and manage prompts just like they can with software modules. It makes sure that the language model behaves the same way and works the same way everywhere. Standardizing things early makes it easier for AI teams to work together and cuts down on duplication. Version management makes it easy to keep track of, test, and go back to older versions. Developers can find out which changes made the model more or less accurate. Automated CI/CD pipelines do a great job of managing testing, deployment, and validation.
This automation speeds up delivery processes and gets rid of human error. Prompt SDKs work well with repositories, which makes sure that version histories are clean. Every update follows rules that make things more open and reliable. In the end, modular prompts make AI development better for the long run by making it more creative, scalable, and easier to regulate quality.
The Function of Prompt Toolchains
Prompt toolchains create a single place to keep an eye on the whole prompt lifetime. They put deployment frameworks, validation tools, and SDKs together into one solution that works together. These toolchains’ automation, scalability, and discipline are good for prompt engineering. Developers can easily edit, lint, simulate, and evaluate prompt performance. This systematic method makes sure that prompts meet tight standards before they are deployed. You can think of toolchains as the DevOps layer for timely engineering tasks. They provide version control, continuous optimization cycles, and automated testing. Toolchains help motivate teams work together well by giving them shared sight and control.
Quality assurance is easier to measure, repeat, and less likely to make mistakes when procedures are followed consistently. Quick toolchains help you go from being ready for production to trying new things. They make sure that every prompt they use is reliable, useful, and has been tested for real-world use.
From Prompt Chaos to Organized Growth
When prompt management isn’t organized, Poor organization of prompt management often causes confusion and inefficiency. Different teams can reuse or change prompts without always working together. When prompts overlap, they can lead to inconsistent answers and repetitive reasoning. Different versions of AI make it behave differently depending on the environment. Slightly changing the language could disrupt procedures or alter the planned results. Prompt toolchains set things straight by adding centralized version control systems. They have a well-organized set of reusable prompts with clear instructions. Dependency graphs show how things are connected and ensure that modules work together. Before release, the system automatically checks, compares, and tests every prompt. Strict governance rules ensure that teams complete approval and ownership processes on time.
Version tracking makes sure that you can experiment safely without hurting production performance. This planned process turns random chaos into development that can be scaled and predicted. Companies make their AI processes more effective, reliable, and easy to control.
Testing and Validating Quickly
Prompt testing is needed to make sure that things work reliably and consistently. Modern Prompt SDKs now come with integrated testing environments and validation suites. These tools do a good job of simulating how a model behaves with different inputs and conditions. Developers can accurately measure output stability, latency, bias, and accuracy. Automated pipelines run prompt tests before production deployment starts. This prevents unreliable or untested prompts from being used in real life. Like software unit testing, prompt validation finds logical or language errors early. Ongoing testing makes sure that prompts always give safe and predictable answers. It also makes it easier to make changes and improve performance across multiple models quickly. Testing the system thoroughly makes people more confident in its scalability and responsiveness. Structured validation makes prompt engineering quality-driven, repeatable, and disciplined. Because of all this testing, prompt creation becomes a dependable way to develop.
Setting Parameters and Environment Variables
To be flexible, prompts often use dynamic, context-based variables. Parameterization makes it possible to change inputs in a flexible and useful way for many situations. It’s easy for developers to define placeholders like {product_name}, {user_goal}, and {customer_query}. These placeholders change automatically based on the information about the environment or the runtime variables provided. This method makes it easier to reuse across many AI projects and workflows quickly. Prompt SDKs use controlled environment settings to safely deal with variable injection. Sensitive information, such as passwords or API keys, is kept safe while in use. When developers switch environments, they don’t have to rewrite or display prompt data manually.
This consistency helps ensure that things work well in testing, production, and development environments. It lowers the chance of human error while making sure that the system is secure, portable, and easy to configure across the board. In general, parameterization and environment variables make things more reliable and scalable quickly.
Quickly Managing Dependencies
Modern AI systems often depend on a multitude of interconnected stimuli functioning in unison. Each module helps with a specific operational or conversational task in the system. For example, a chatbot might ask questions, give advice on how to fix problems, and start small talk. To avoid getting answers that are the same or don’t make sense, this kind of coordination needs careful planning. Dependency management makes sure that all of the prompts work together and don’t get in the way of workflows. Prompt toolchains take care of imports, sharing variables, and rules for compatibility all by themselves. As projects grow or change, they keep the logical connections between the modules the same.
Hierarchical dependency mapping helps developers keep better track of how prompts are related to each other. Version tracking makes sure that upgrades or optimizations will work with all versions. This methodical approach makes maintenance, scalability, and dependability better in complex AI environments. In the end, good dependency management leads to smoother interactions and AI behavior that is easier to predict.
The Move Toward Prompt APIs
Because of the move toward Prompt APIs, developers are changing the way they make AI-powered apps. Thanks to modern SDKs, prompts can now be offered as callable APIs. It’s easy to add these APIs to existing systems and automation workflows. Each prompt has its own inputs and outputs and works like a module that runs in the cloud. This methodical approach makes it easier to use AI on different platforms and in different workflows. Standardized API calls let developers start prompts through code. It helps AI services and regular microservices talk to each other more easily. Also, prompt APIs make projects more modular, scalable, and easy to maintain. They make it easier to work with multiple models and reduce the need for manual setup.
Prompts are becoming important parts of software ecosystems. Prompt APIs are enabling people around the world to use more advanced Prompt-as-a-Service models. This breakthrough has given intelligent systems structure, adaptability, and dependability.
Combining with traditional development workflows
These days, it’s easy to add Prompt SDKs to existing development methods and ecosystems. They work with tools like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, and Docker to automate tasks. This smooth integration has made prompts more in line with standard software engineering practices. Developers can use well-known CI/CD pipelines to save, test, and deploy prompts. Automated quality checks, testing, and reviews are done on prompts just like they are on regular code. Because of this alignment, AI parts will always follow the same rules for governance and control. Version control ensures that prompt logic is in sync across all distributed development teams. Integration also makes it easier for AI models to do continuous delivery, rollback, and dependency tracking. It changes ad hoc experimentation into formal technical discipline and quick management. This marriage led to the creation of PromptOps, which combines DevOps ideas with the best practices of prompt engineering.
Working together with developers and non-technical teams
Prompt SDKs are helping developers and teams that don’t know much about technology work together. These SDKs make it easy for writers, marketers, designers, and engineers to work together. Each contributor can focus on their own area of expertise while making strong AI prompts. Writers work on tone and clarity while developers work on logic and structure. Designers make sure that the prompt fits with the brand’s identity and the goals of the user experience. Version control keeps everyone up to date on the most recent and important changes.
To make sure everything is clear, we carefully note, review, and compile every change. This method encourages open participation without sacrificing quality or technical stability. More and more, non-technical professionals are having an impact on how AI creates experiences and content. Prompt SDKs make it easier for people in the technical and creative fields to work together in an organized way. When people work together, they make AI-driven communication results that are more creative, reliable, and consistent.
Modular prompts for environments with more than one model
More and more businesses are using AI models for a wide range of tasks. Every model works best in certain situations, so design needs to be quick, flexible, and adaptable. Modular prompts make it easier to use the same logic in more than one AI system. Developers can make each module work better with Gemini, Claude, GPT, or other systems. Because of the same structure, all integrations will always have the same purpose and results. Rapid SDKs handle different syntax, which makes it easier to switch between different model ecosystems. They make an interface that works well together and is easy to maintain and grow.
This flexibility makes it possible to try things out quickly with little rework or loss of performance. Teams can compare results between models without having to change their workflows completely. This modular approach makes it less necessary to depend on just one AI provider. It encourages creativity, portability, and long-term sustainability in changing AI settings.
AI Agents Using Prompt Toolchains
AI agents need well-designed and organized prompt systems. With prompt SDKs, developers can make modular templates for the personalities of agents. Each template sets the tone, logic, and context for the AI to work well consistently. Toolchains take care of conversational state, retries, and the flow of interactions on their own. They use memory systems to keep things going between different user sessions. This methodical process ensures that agent responses will be consistent and repeatable over time. Developers can change or update some prompt modules without having to start from scratch. It lets you deploy more intelligent, more flexible agents faster and iterate more quickly. Also, prompt toolchains come with testing frameworks that can check for accuracy and consistency.
By automating version management, developers can reduce output drift and human error. AI agents grow naturally through regular, data-driven, and timely monitoring and changes. Structured systems make intelligent agents scalable, dependable, and ready for the future.
Why This Method Is Important
Prompt SDKs are changing the way developers make, test, and use AI workflows. Instead of writing prompts randomly, they use organized, code-based development methods. By treating prompts like modular code, developers can have more control and consistency. This framework makes sure that performance will be the same across a lot of models and environments. Companies can scale AI systems with more trust and openness. With version control, teams can monitor, check, and manage rapid evolution. Automation speeds up testing, validation, and deployment by eliminating the need for manual work. These steps help prevent prompts from causing mistakes and performance drift in production. It is easier to measure, keep up with, and copy innovation around the world. This method turns prompt engineering into a planned process for making software. Ultimately, it makes AI development more professional by combining engineering accuracy with creativity.
Final Thoughts
One big step forward in AI development is treating prompts like code modules. It goes from trial and error to systematic, scalable engineering methods. Prompt SDKs add version control, consistency, and openness to the process of making prompts. They transform text prompts that don’t change into reusable and programmable parts. Toolchains quickly and accurately automate deployment, validation, and testing. This change has made it easier for teams to handle AI workflows. Like modern software systems, prompts now have structured lifecycles. Ongoing testing and integration make sure that reliability and performance are always at their best.
Developers have complete control over the version history and how quickly they respond. It is easier for people with technical and creative skills to work together. Engineers will build future AI systems on well-documented and flexible prompt architectures. This change demonstrates AI engineering’s progress, as it now relies on reusable intelligent components.

I’m a passionate blogger and senior website developer with an MPhil in Computer Science, blending technical expertise with a deep appreciation for the art of storytelling. With advanced knowledge of English literature, I craft content that bridges creativity and technology, offering readers valuable insights and engaging narratives. Whether building dynamic websites or exploring thought-provoking ideas through my blog, I’m driven by a commitment to innovation, clarity, and impactful communication.